Server scale up - Production Server Spec for Special Event New
Zoom session to explain each items on this doc
https://us06web.zoom.us/rec/share/ezgXk4L-p5-NLJ1n_qvA59SwIHE942TgMipWcy06qYc8rWMrv8xyFr_PjNAmAyUz.HTLAkP2Xcegf2BP6 Passcode: @&Na$5f6
Update Event start time and end time
Update Redis max connection automatically
FIX ME Login to any sidekiq-default pod as an example
kubectl exec hungryhub-sidekiq-default-785c4ffbf6-68lzv -n hungryhub -c service -ti -- bash
execute bin/rc inside the pod then execute these commands to disable some features that slow down servers
AdminSetting.event_start_time = "#{Time.thai_time.to_date} 09:00"
AdminSetting.event_end_time = "#{Time.thai_time.to_date} 11:00"
AdminSetting.redis_lru_max_connection = 300
AdminSetting.redis_lru_timeout = 3
Flipper.enable :reviews_v2
Then revert it later when the event is over
AdminSetting.redis_lru_max_connection = 100
AdminSetting.redis_lru_timeout = 3
Flipper.disable :reviews_v2
We update following configuration in Jenkins
URL: jenkins.hungryhub.com ask Saiqul for the account
Following setting maybe outdated already
Sidekiq
normal days: cache.m6g.large event day: cache.m6g.xlarge (not r instance)
LRU
normal days: m6g.xlarge event days: m6g.8xlarge
Caution:
Flush the Redis before we downgrade it. the current memory is bigger than what Xlarge machine can store. so we need to clean the memory first
redis-cli -h redis host flushall async
Login to any hh-server pod, install redis-cli
Memcached
normal days: 2 event days: 20
Upgrade RDS
Booking production:
normal days:
- primary: r5.xlarge
- Reader:
- auto scaling 40%
- 2 replicas event days:
- primary: r5.xlarge
- Reader:
- auto scaling 25%
- 3 replicas even
Change DB autoscaling setting to be
Huginn:
upgrade hh-production-db instance from db.m5.2xlarge jadi db.m5.12xlarge
Update Auto Scaling Group
use 50% spot, 50% on demand
Update Node groups
normal days, min 2 event days min 20
HH Server Pods
normal days:
- min 10
- max 1000 event days:
- min 750
- max 1500
Sidekiq Critical Pods
normal days:
- min 2
- max 20 event days:
- min 5
- max 20
Scale up Huginn server pods
normal days: 2 event days 5
Scale up Huginn DB
normal days t3.small event days: t3.large
Server scale up/down using Jenkins
When Jenkins server is down, we can scale up/down manually. see this doc: Private (https://app.clickup.com/9003122396/docs/8ca1fpw-14210/8ca1fpw-14290)
Open https://jenkins.hungryhub.com/job/scale-infra/ and click "Build with Parameters" or "Schedule Build" button from the sidebar
For the scheduled build, it uses Bangkok timezone.

Components
There are few components that we can scale up

SSM
We put environment variables to SSM. Some variables have different value between Normal event and Big event.
RDS
This is to change all RDS DB.
If we scale up/down during low-traffic hours, then we can use Jenkins. Otherwise, hh-server will be very slow because we don't implement the Blue-Green Deployment strategy to our RDS Aurora yet.
check scripts/scale_down_rds_aurora.sh script in our terraform code, to scale down the RDS during busy hours.
Redis
This is to change all Redis instances.
If we scale up/down during low-traffic hours, then we can use Jenkins. Otherwise, hh-server will be very slow because we don't use Redis cluster strategy yet.
check script scripts/manual_blue_green_deployment_for_inventory_redis.sh and scripts/manual_blue_green_deployment_for_app_lru_redis.sh in our terraform code, to scale down the Redis instances during busy hours.
Memcache
This is to scale up/down our memcached elasticache instance. so far we just adding/removing more memcached instances to handle the event.
EKS, Hungryhub-apps, EKS-services
These components are related to Kubernetes. So far there is no issue if we change the infra spec anytime.
Auto Approved
 If the value is "No", then we need to confirm the button before Jenkins executes the pipeline
If the value is "No", then we need to confirm the button before Jenkins executes the pipeline
Environment
 dev is sandbox aws account - hhstaging.dev
dev is sandbox aws account - hhstaging.dev
Event Types
 We have 3 types
We have 3 types
- big
- normal
- no event
if normal_event is false and big_event is false, then it means we use
no eventconfig
Normal event is supposed to handle 20k request per minutes Big event is supposed to handle 150k request per minutes (we tested this already in 10.10 2023 flash sale event)
Date
 We installed
We installed SMTP plugin to notify us whenever a pipeline is succeed or failed
This date data will be added to the email. just to add more information to the email.
Because it's confusing when we got many emails from Jenkins and we don't know it's for which pipeline. This date field is useful for Scheduled Pipeline
Current issues
hh-server app depends on DB, Redis, and Memcached Changing AWS RDS and Redis instance type would cause some connection issues in the hh-server app so typically, we should create a new instance of Redis/DB, and let hh-server connect to the new instances. Once the hh-server is connected to the new instance, we can modify the original instance and then change the connection back to the original instance when the modification is done.
Devops Team
Host list
- CI server 78.47.203.51
- VPS staging 62.55.33.126
- data-team-server 135.181.80.79
- Host fast-api 18.142.150.51
- Host hh-menu HostName 65.108.213.91
- Host madison HostName 5.161.124.128
CI CD Runners
We have two CI CD system currently
- Gitlab
- Github Those to system use the same Runner, the IP address is 78.47.203.51 once you have given the access, you can login to
ssh root@78.47.203.51
What to do when Gitlab CI doesnt work
usually it caused by the storage is full, you can clear it by
docker system prune -a
docker volume prune
What to do when Github Actions doesnt work
usually because the runner doesnt work
cd /home/github_runner
./svc.sh start # if doesnt work, try below
./run.sh
validate it by checking the running process

ps aux | grep github_runn
ps aux | grep run.sh
How to give someone access to kube cluster
- Create the IAM User from root account and give them EKS access role (accessKubernetesApi) (group kube-cluster-only)
- Update configmap on the cluster and add the IAM user
kubectl edit configmap aws-auth -n kube-system
mapUsers: |
- "userarn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:user/eks-user"
"username": "eks-user"
- Then the user should update kubeconfig
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name <cluster>
Host List (Our IP Address) - Vendor has to Whitelist these IP Addresses
- Prod
- AWS Sandbox
- For sandbox the IP is dynamic to reduce cost
- CI server 78.47.203.51
- Host fast-api 209.97.160.103
- Digitalocean Kubernetes Cluster
- do-staging 159.223.70.101
-
* do-production
152.42.213.61
CI CD system
We have 3 CI CD system currently
- AWS Codepipeline
- This CI CD is to build docker image for Kubernetes cluster and other services
- Github runner self-hosted on Mac Mini
- This CI CD is to build IOS and android apps
- Jenkins
- This CI CD is to build infra using terraform IaC
How to give someone access to kube cluster
- Create the IAM User from root account and give them EKS access role (accessKubernetesApi) (group kube-cluster-only)
- Update configmap on the cluster and add the IAM user (should add into terraform too)
kubectl edit configmap aws-auth -n kube-system
mapUsers: |
- "userarn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:user/eks-user"
"username": "eks-user"
- Then the user should update kubeconfig
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name <cluster>
When pipeline terraform remote lock state failed
- Delete all dynamodb item

- Re-run the terraform pipeline on codepipeline
Robusta
- robusta prod
- channel #monitoring-k8s-prod
- robusta sandbox
- channel #monitoring-k8s
- robusta digitalocean
- channel #monitoring-k8s
Nameserver for AWS Route53 and cloudflare
AWS Route53
- ns-620.awsdns-13.net
- ns-1858.awsdns-40.co.uk
- ns-20.awsdns-02.com
- ns-1263.awsdns-29.org Cloudflare
- alla.ns.cloudflare.com
- lee.ns.cloudflare.com
Architectures
HH-Server
Recommendation Service
domain: https://rec.hungryhub.com/ repo: https://github.com/hungryhub-team/rec-service diagram:
GMT20221117-103412_Recording.m4a
HH Menu
GMT20220428-081155_Recording.m4a
AOA WebView
Currently, AOA still wants to use the old UI, so we can't merge it into the master because the master already uses the new UI. To address this, we have created a new production deployment called "aoa-master". We will implement the new UI once AOA agrees to adopt it in the future.
Staging
Domain: https://hh-aoa.netlify.app Repo: https://github.com/hungryhub-team/hh-web-new-ui/tree/feat/aoa-integration
Production
Domain: https://hh-aoa-production.netlify.app Repo: https://github.com/hungryhub-team/hh-web-new-ui/tree/aoa-master
Plumber
Repo: https://github.com/hungryhub-team/plumbers Domain: http://plumber.utility for every cluster Docs: https://github.com/hungryhub-team/plumbers/blob/main/docs/index.md
Reserve With Google
There're several error that might be happen when uploading feed in reserve with google.
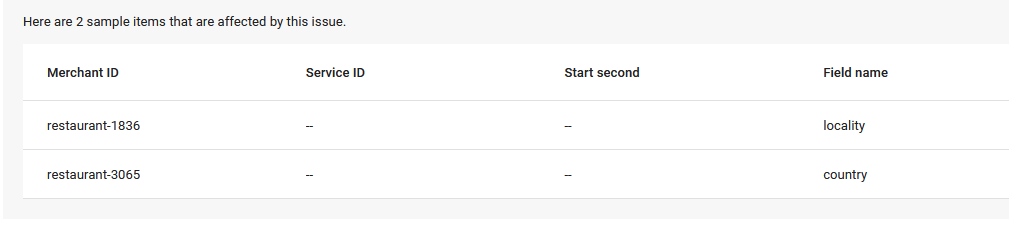
locality
Usually this happen because google can get any city or state from latitude and longitude that we sent. In this example restaurant 1836 (The Coffee Club Day Inn (Phuket)) when I check admin the latitude and longitude seems wrong:
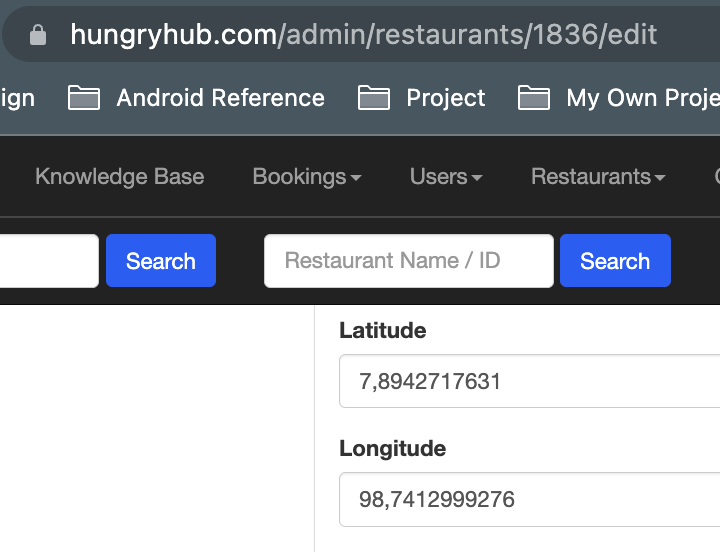 If we manually type the google maps link with that latitude and longitude will open the sea instead of phuket.
https://www.google.com/maps/@7.8942718,98.7412999276,14z?entry=ttu
If we manually type the google maps link with that latitude and longitude will open the sea instead of phuket.
https://www.google.com/maps/@7.8942718,98.7412999276,14z?entry=ttu
If this case happen, we need to update our restaurant data from admin dashboard and set the right latitude and longitude.
country
This happen when we put the wrong phone number country code in our restaurant setting.
How to Match Location
After we successfully upload our restaurant feed the data will available in Inventory data:
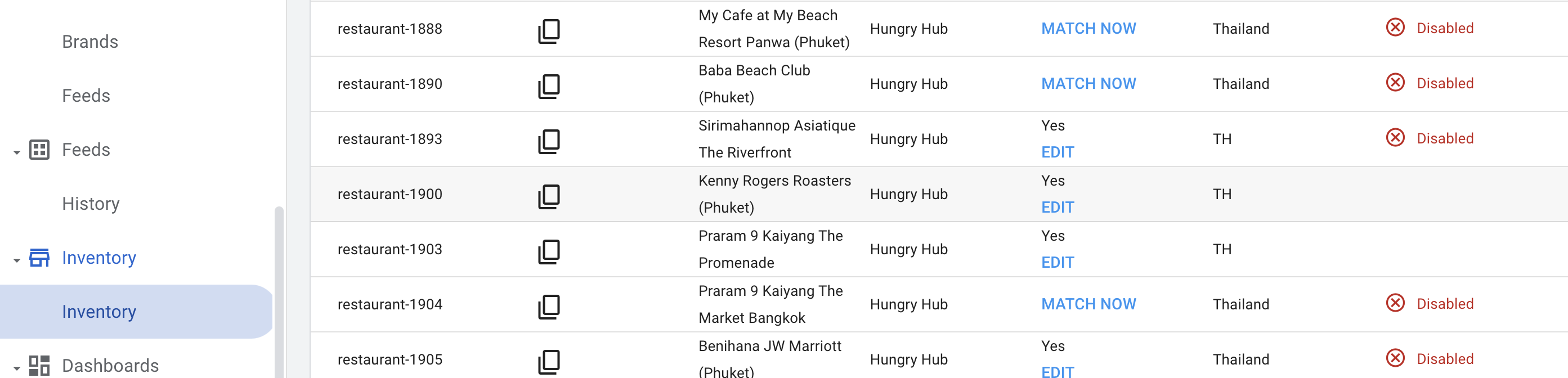
But there is a case where a restaurant doesn't match with any google map data. So we need to fix it manually.
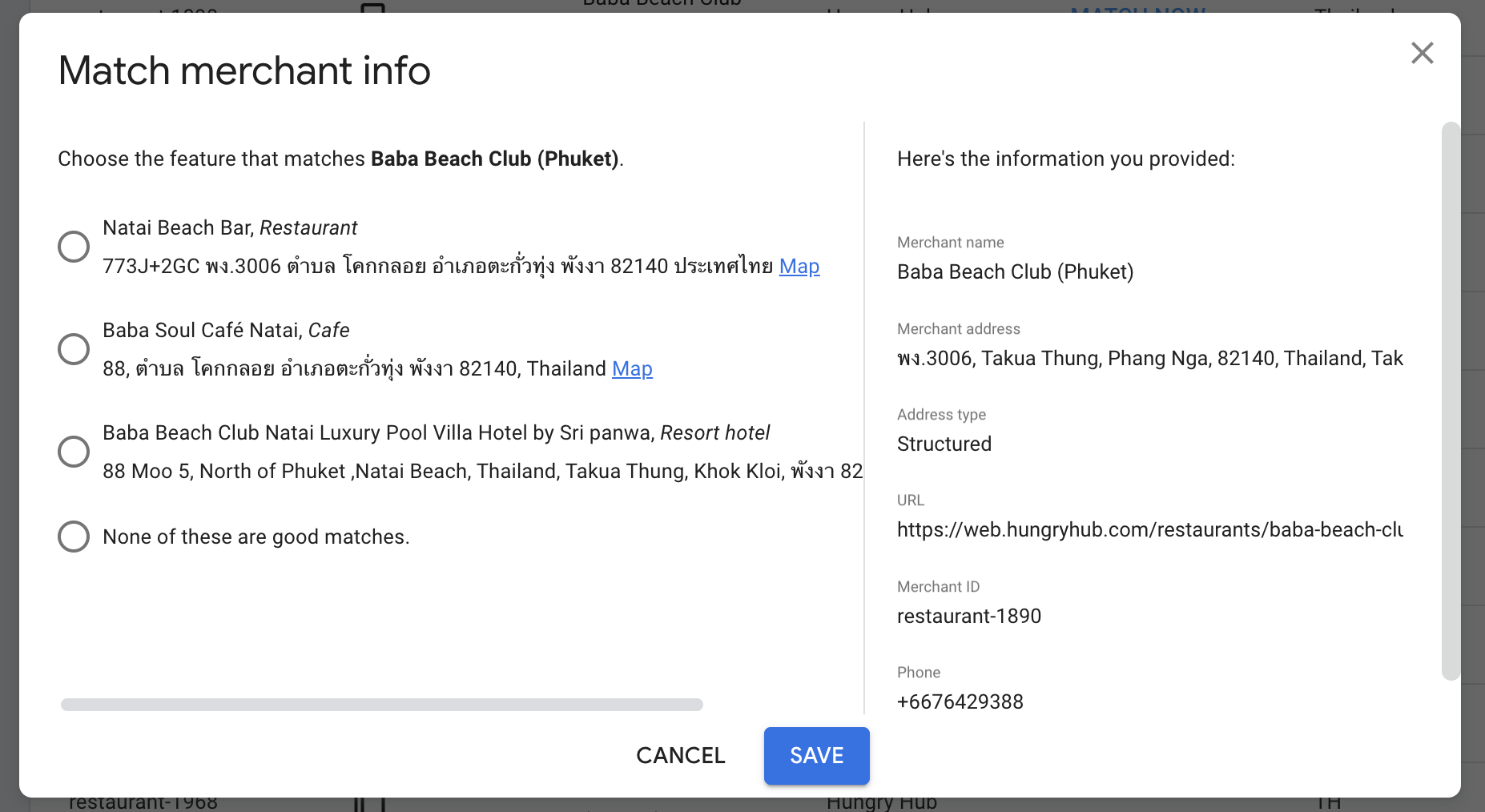 We can click match now, select the right map data and then click save.
We can click match now, select the right map data and then click save.
Backend Team
Private (https://app.clickup.com/9003122396/docs/8ca1fpw-12905/8ca1fpw-34296) Private (https://app.clickup.com/9003122396/docs/8ca1fpw-12905/8ca1fpw-34316)
Database configuration
Rails app uses config/database.yml to store the DB connection config.
the database.yml on production environment is generated by buildspec.yaml
- aws ssm get-parameter --region $AWS_REGION --name "/$Environment/hh_server_config_database" --with-decryption --output text --query Parameter.Value > config/database.yml
it means the codepipeline script will get the config from Secret manager (ssm) then write a database.yml
before starting the pod (read k8s pod on the internet), we modify the database configuration on the container's args (manifest/prod/hungryhub-server.yml):
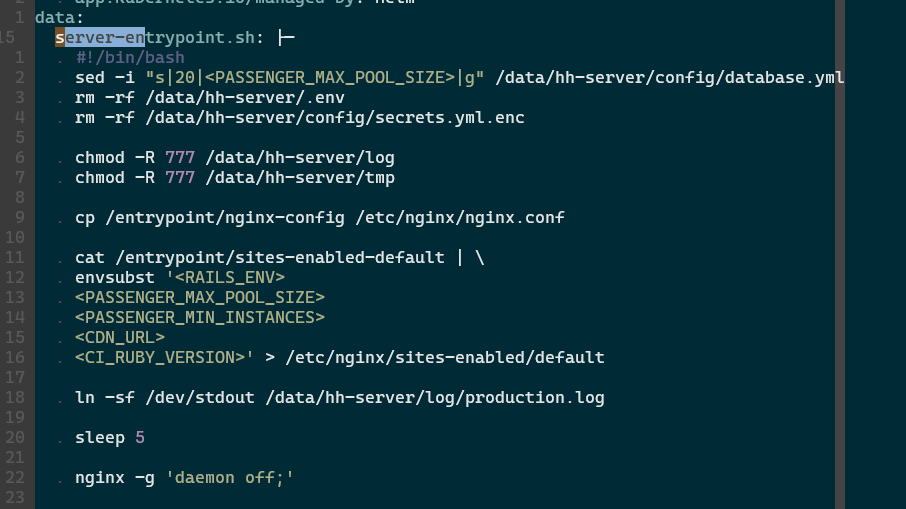
 server-entrypoint.sh is a script that generated dynamically on manifest/prod/hungryhub-server.yml
server-entrypoint.sh is a script that generated dynamically on manifest/prod/hungryhub-server.yml
 we can see that there is a
we can see that there is a sed command to update the DB pool.
original file:
production:
adapter: <%= ENV.fetch('DB_ADAPTER') { 'mysql2' } %>
encoding: utf8mb4
charset: utf8mb4
collation: utf8mb4_unicode_ci
username: <%= ENV['MYSQL_USER'] || raise('undefined db username') %>
password: <%= ENV['MYSQL_PASSWORD'] || raise('undefined db password') %>
database: booking_production
host: <%= ENV['MYSQL_SERVER_HOST'] %>
port: <%= ENV['MYSQL_PORT'] %>
pool: 20
makara:
id: mysql
blacklist_duration: 5
primary_ttl: 5
primary_strategy: round_robin
sticky: true
connections:
- role: master
host: ${master}
url: 'mysql2://${username}:${password}@${master}:3306/booking_production'
disable_blacklist: true
- role: slave
host: ${slave1}
url: 'mysql2://${username}:${password}@${slave1}:3306/booking_production'
modified file:
production:
adapter: <%= ENV.fetch('DB_ADAPTER') { 'mysql2' } %>
encoding: utf8mb4
charset: utf8mb4
collation: utf8mb4_unicode_ci
username: <%= ENV['MYSQL_USER'] || raise('undefined db username') %>
password: <%= ENV['MYSQL_PASSWORD'] || raise('undefined db password') %>
database: booking_production
host: <%= ENV['MYSQL_SERVER_HOST'] %>
port: <%= ENV['MYSQL_PORT'] %>
pool: 1
makara:
id: mysql
blacklist_duration: 5
primary_ttl: 5
primary_strategy: round_robin
sticky: true
connections:
- role: master
host: <%= ENV['MYSQL_MASTER_HOST'] %>
url: <%= ENV['MYSQL_MASTER_URL'] %>
disable_blacklist: true
- role: slave
host: <%= ENV['MYSQL_SLAVE_HOST'] %>
url: <%= ENV['MYSQL_SLAVE_URL'] %>
Web server
We use a Passenger web server to serve any HTTP requests
passenger has passenger-status command to check the running processes:
 The screenshot above shows that we use one Passenger process to respond to all incoming requests. Adding more processes will consume more CPU and Memory, so we need to calculate the CPU and Memory usage first to decide how many processes we can use in a single server. If the server has a lot of CPU and Memory, then we can use more processes.
The screenshot above shows that we use one Passenger process to respond to all incoming requests. Adding more processes will consume more CPU and Memory, so we need to calculate the CPU and Memory usage first to decide how many processes we can use in a single server. If the server has a lot of CPU and Memory, then we can use more processes.